
GEOSPHERE: solid layer of the Earth. It all the rocks and land that make up the Earth. It forms the continents and landforms, also the ocean floor.
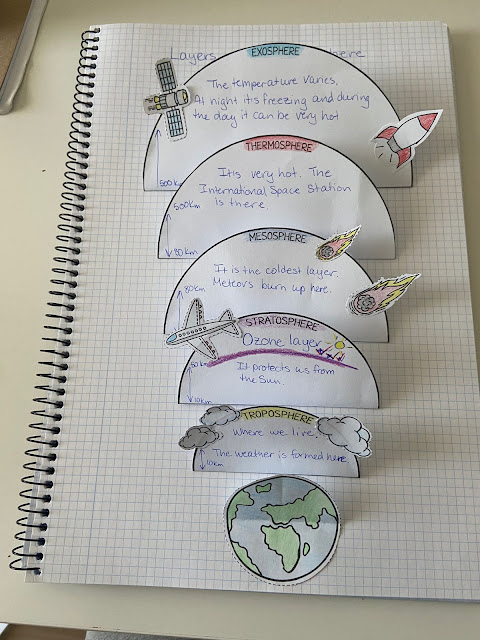
ATMOSPHERE: layer of gases that surround the Earth (78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases)
HYDROSPHERE: layer of water (70% salt water, 30% fresh water). We can find water in the oceans, rivers, lakes, glaciers and clouds.
BIOSPHERE: all living things on Earth


MAP: It is a flat representation of the Earth.
GLOBE: It is a spherical representation of the Earth.
BOTH MAPS AND GLOBES HAVE IMAGINARY LINES
The world is divide in 24 time zones, each of which is about 15 degrees of longitude wide, and each of which represents one hour of time. The numbers on the map indicate how many hours one must add to or subtract from the local time to get the time at the Greenwich meridian.

TYPES OF MAPS
A map represents the Earth or a part of it on a flat surface. It is almost impossible to show a sphere as a flat shape so maps are always distorted. There are many types of maps. We are going to study:
2.1 PHYSICAL MAPS: they show the location of important natural features such as mountains, rivers and lakes. Different colours are used to show the elevation of different areas of land.
2.2 POLITICAL MAPS: they show different areas of land divided by political borders. Political maps show land divided into different areas and countries. They also show the capital cities of countries and other important cities.
2.3 STREET MAPS: A street map is a map of a smaller area, such as a town or a city. They show natural features, like forests and rivers, and man-made features, such as hospitals, roads and parks. We use these maps to find directions to places we want to go to.
PARTS OF A MAP
Maps are important tools that show us different places on Earth. Each part of a map provides important information. To read a map, you need to understand the different parts.
THE SCALE OF A MAP
The scale of a map shows the real distance between two places.
EXAMPLE:
4cm : 1 Km
( in the map ) ( in real life)
If the scale is 4 cm: 1 Km, it means that 4 cm in the map correspond to 1 km in real life.
DRAW A MAP ON YOUR NOTEBOOK
LET´S REVISE AND PLAY
SUMMARY


WEATHER describes atmospheric phenomena,such as wind, rain and temperature, at specific time in an specific place. Weather can change at any time, even during the same day.
CLIMATE describes the typical weather condition of a place over a long period of time. Climate is related to the water cycle.

DO THIS QUIZ, ARE YOU READY?
ACTIVITY 1 CLICK HERE


SPAIN´S CLIMATE ZONES ACTIVITY 1 CLICK HERE
































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario